You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
The AQI is dropping in New York City and Boston ... again.
One thing New Yorkers could always reliably lord over urban Californians was our air. No, our city isn’t perfect — we manage our trash by piling it on the curb and have this pesky thing called “winter” — but at least in recent years our metro area beat San Francisco, Sacramento, and smoggy Los Angeles when it came to the particulates we inhale.
It brings me no joy to report, then, that this spring, tides have turned. Or at least the winds have. East Coasters have evidently inhaled more smoke than most Californians in 2023 due to a quiet start to the wildfire season out West and an explosive start to the one upwind of us in Alberta, Saskatchewan, and now Nova Scotia.
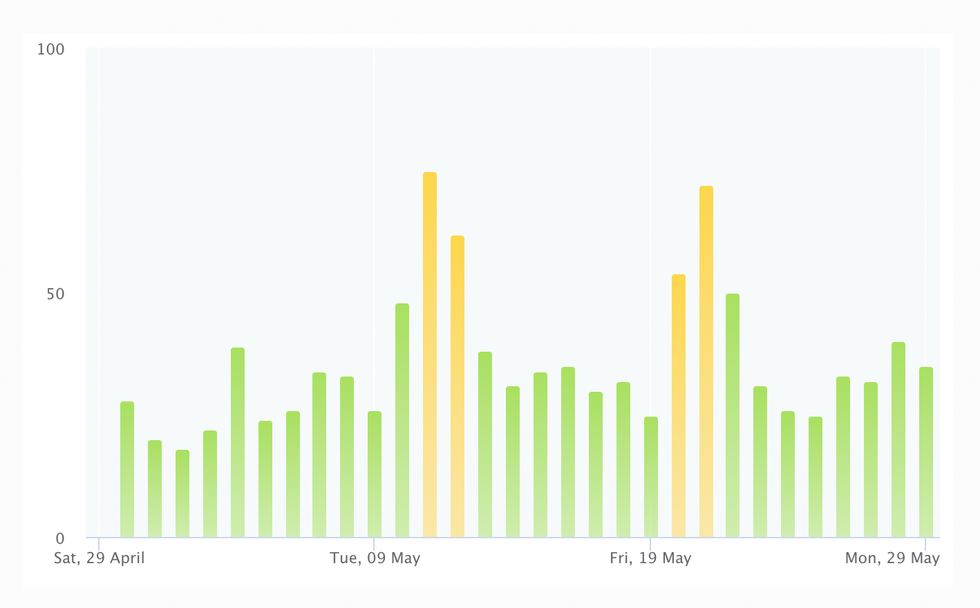
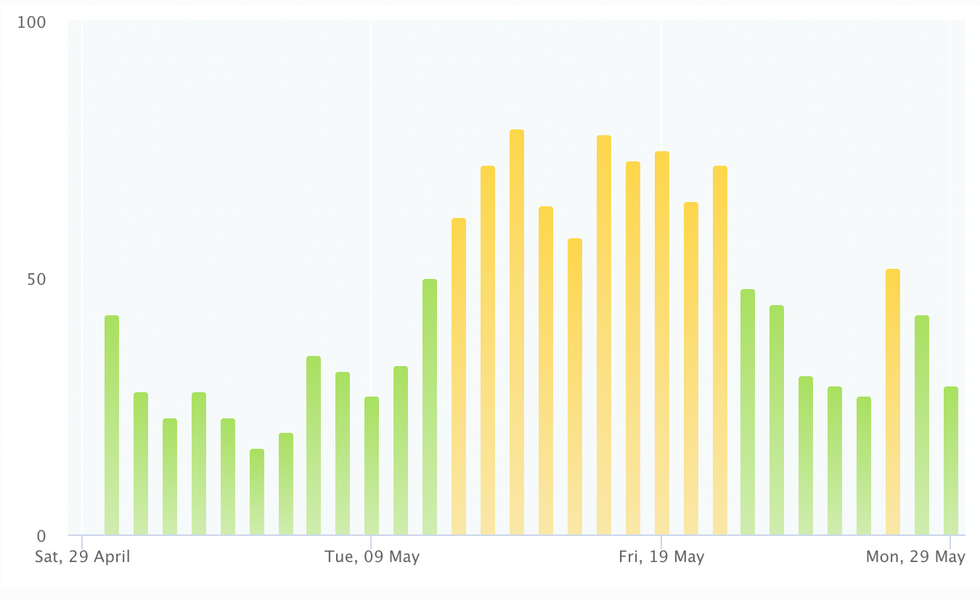
Here’s what the historic AQI has looked like in New York since late April (the yellow spikes mark smoky days):
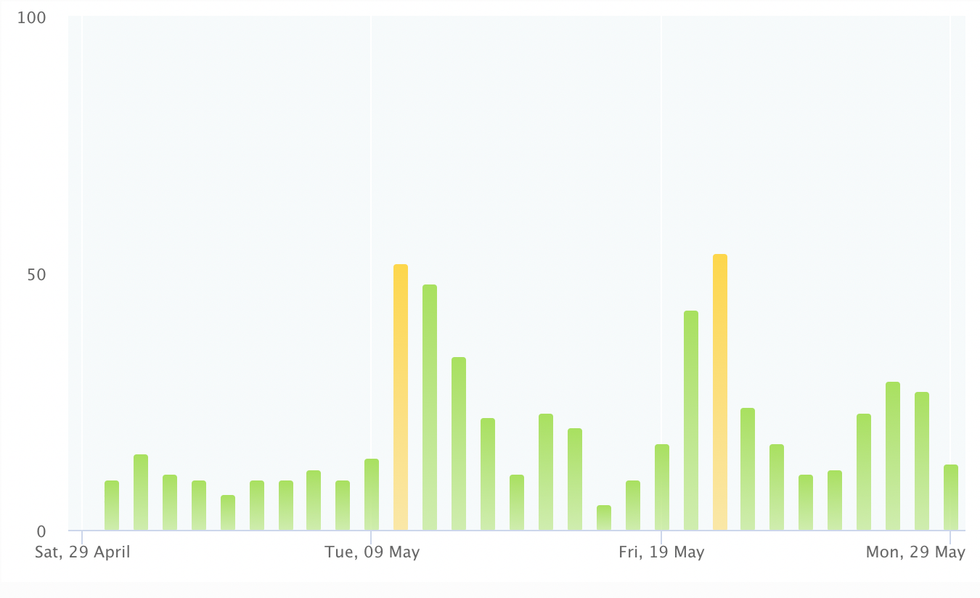
And here’s what it’s looked like in Boston:
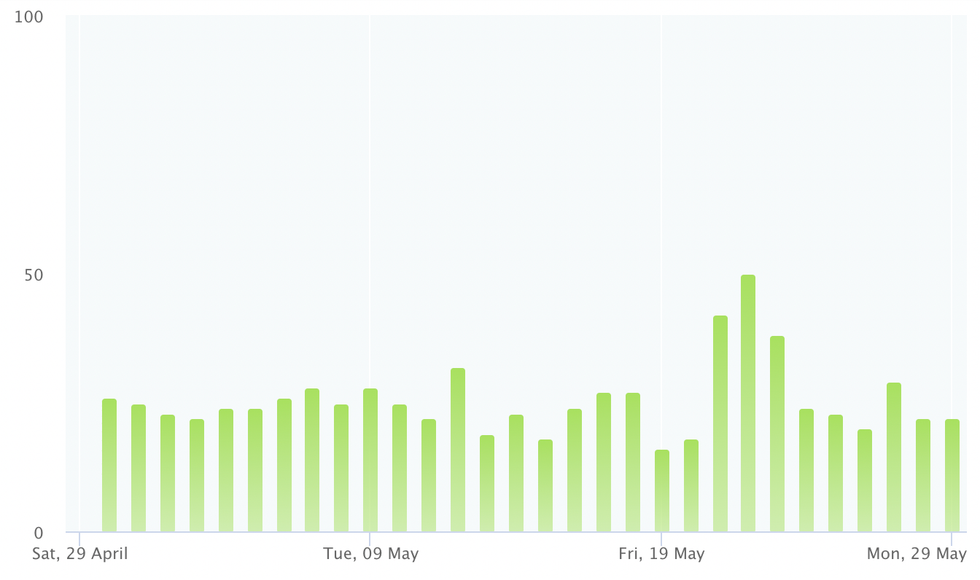
By comparison, here is San Francisco:
And Sacramento (note the AQI scale here has changed on the left to out of 50):

Though the air quality in Los Angeles has been significantly worse than the AQI in New York or Boston this spring, the yellow “moderate” AQI columns below overlap with a period of heavy urban pollution, rather than wildfire smoke. The yellow columns on the East Coast AQI charts, by contrast, match periods when wildfire smoke blew in from Canada.
New Yorkers might be surprised to hear they’ve experienced more smoked-tinted sunrises and sunsets this year than Californians, but it checks out: There have been no major (more than 1,000 acres) fires in California yet in 2023. While that might seem unusual, it isn’t; what is unusual are the years like 2021, when the season started in early spring. But 2023 is so far looking to be an average year for California wildfires, which means large burns and regional smoke pollution aren’t expected in the Golden State until late summer and early fall (of course, an El Niño could throw all of this into question).
Meanwhile, in Canada, it is fire season — and it’s been an especially bad one. Almost 5 million acres have already burned, with Alberta on track to have its worst fire year ever. Though smoke from the Canadian fires has blown into a number of northern U.S. states, including Washington and Montana, the jet stream generally carries air east, with some particulate matter making it as far as Boston and New York. (Winds have likewise prevented Canadian wildfire smoke from making it as far southwest as California, hence the unexpected smoke disparity). Over the weekend, a new fire also started in Nova Scotia, causing some 16,000 evacuations around Halifax; the wind has blown much of that smoke southwest, with residents of Connecticut and Massachusetts reporting on Tuesday that they could smell and even taste the smoke.
\u201cSMOKE PLUME...\nFrom Nova Scotia #wildfires creating hazy skies over Boston... sky is much bluer over Worcester. Forecast details coming up at noon on #WCVB\u201d— Cindy Fitzgibbon (@Cindy Fitzgibbon) 1685461877
\u201cAfternoon update... smoke plume continues to move west. There will be about a 4 hour period of reduced air quality. You may smell smoke as this passes through and some fire departments have fielded calls from people wondering what it is. #fox61\u201d— Ryan Breton (@Ryan Breton) 1685460842
The smoke from Canada is also, of course, causing the air quality across the East Coast to plunge. This is not in and of itself a rare occurrence: In 2021, smoke from fires in California likewise caused New York City to experience its worst AQI in 15 years.
East Coast residents may nevertheless feel — incorrectly — that they’re isolated from the dangers of wildfires. In truth, roughly three-quarters of smoke-related asthma cases and deaths occur east of the Rocky Mountains, one study found, due to both population density and wind patterns. Another pre-print study by Stanford researchers that was recently referenced by David Wallace-Wells in The New York Times found similarly that 60 percent of the smoke impact from U.S. wildfires occurs in a different state than the one where the fire is actually burning. Separately, a University of Washington study found that people were 1% more likely to die from “nontraumatic” causes like a heart attack or stroke on a day when they were exposed to wildfire smoke — and 2% more likely the day after.
New Yorkers live in the superior coastal city, but we shouldn’t get too smug about our air. Thinking we’re somehow immune to the West’s smoke problems is patently false
and getting falser. Besides, why should Angelenos get to have all the fun? It’s only fair that we get to obsess over our PurpleAir score, too.
Get the best of Heatmap delivered to your inbox:
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Current conditions: Yosemite could get 9 inches of snow between now and Sunday • Temperatures will rise to as high as 104 degrees Fahrenheit in Ashgabat, Turkmenistan, as Central and Southeast Asia continue to bake in a heatwave • Hail, tornadoes, and severe thunderstorms will pummel the U.S. Heartland into early next week.
It was a busy week of earnings calls for the clean energy sector, which, as a whole, saw investment dip by nearly $8 billion in the first three months of the year. Tariffs — especially as they impact the battery supply chain — as well as changes to federal policy under the new administration and electricity demand were the major themes of the week, my colleague Matthew Zeitlin wrote.
Like companies across many different sectors, inverter and battery maker Enphase, turbine manufacturer GE Vernova, Tesla, and the utility NextEra all mentioned the tariffs in their earnings reports and calls. Enphase, for one, is bracing for as much as 8% knocked off its gross margin by the third quarter, while Tesla’s highly-anticipated call managed expectations for the rest of the year, with the company citing the difficulty measuring “the impacts of global trade policy on the automotive and energy supply chains, our cost structure, and demand for durable goods and related services.” Meanwhile, on Thursday, Xcel Energy — which recently reached settlements for its role in the ignition of the most destructive wildfire in Colorado history and the largest wildfire in Texas history — reported missing first-quarter estimates and feeling the squeeze of high interest rates at a time of soaring, data-center-driven electricity demand.
The Department of Justice’s lawyers warned the Department of Transportation that its case against New York City’s congestion pricing program is likely a loser. We know this because someone mistakenly uploaded the DOJ’s memo into the court record for the Metropolitan Transportation Authority’s lawsuit challenging Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy’s actions. Whoops.
As my colleague Emily Pontecorvo reports, the leaked memo was dated before Duffy announced “he would put a moratorium on any new federal approvals for transit projects in Manhattan until the state shut down the tolling program.” But as Emily goes on to say, the memo “warns that continuing down this route could open up both the department and Duffy personally to further probes.” The New York Times adds that the DOT has since replaced the DOJ lawyers who authored the memo and plans to transfer the case to the civil division of the Justice Department in Washington.
More than 100 new cars and vehicles are expected to debut at the 2025 Shanghai Auto Show, which began on Wednesday and runs through next Friday. Of the approximately 1,300 total vehicles on display, 70% are new energy vehicles, according to Gu Chunting, the vice chairman of the Council for the Promotion of International Trade Shanghai, one of the event’s organizers.
The show is already off to an exciting start. Volkswagen is showcasing 50 new models, including three electrified concept vehicles specifically targeted at the Chinese market: the ID. Aura sedan, the ID. Evo SUV, and ID. Era three-row SUV, a hybrid with over 621 miles of range. BYD’s Denza line also premiered its Z, a luxury electric vehicle designed to compete with Tesla and Porsche. “Beauty is in the eye of the beholder, of course, but most people will find the Denza Z to be drop dead gorgeous,” Clean Technica raved.
That’s not all. The Faw Group, a Chinese state-owned car manufacturer, showed off a flying vehicle with a range of 124 miles, while fellow Chinese automaker Changan Automobile announced an autonomous flying car that reportedly already has government approval to transport passengers, per IoT World Today. France’s Le Monde was wowed by China’s innovations all around: “Gone are the days when the vast exhibition space had one hall dedicated to foreign brands and another for Chinese ones. Today, each Chinese group occupies a hall, showcasing domestic brands and leaving only some space for foreigners around the edges.”

In a private ceremony Thursday night, President Trump signed an executive order to “unleash” deep-sea mining. The order — which directs the secretaries of Interior and Commerce to accelerate “the process of renewing and issuing seabed mineral exploration licenses and commercial recovery permits” for the U.S. Outer Continental Shelf and “areas beyond national jurisdiction”— is an attempt to offset China’s dominance of the critical minerals supply chain. Deep-sea mining operations harvest “nodules” that take millions of years to form and contain minerals like nickel, copper, cobalt, and manganese necessary for lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles, among other applications. “For too long, we’ve been over reliant on foreign sources, and today this historic announcement marks a big step in the right direction to onshore these resources that are critical to national homeland security,” a senior administration official told reporters on Thursday, as reported by CNN.
Deep-sea mining is controversial due to how little we know about the ocean’s abyss, including the potential impact of large-scale mining operations on marine biodiversity and carbon sequestration. The United States has largely abstained from the deliberations of the United Nations’ International Seabed Authority, which determines whether and how to mine the seabed for critical minerals. The industrial mining of international waters, as cued up by Trump’s executive order, is opposed by “nearly all other nations,” The New York Times writes, and is “likely to provoke an outcry from America’s rivals and allies alike.”
It has already been a tragic year for wildfires, with more than 57,000 acres of Los Angeles and the surrounding hillsides burned in January. Now, AccuWeather is predicting that fires in the U.S. could “rapidly escalate” and burn up to 9 million acres total this year, well above the historic average of 7 million acres and close to the 8.9 million acres that burned in 2024.
Specifically, AccuWeather predicts an extreme fire season in the Northwest, northern Rockies, Southwest, and South Central states, particularly as late summer and fall approach. “There was plenty of rain and snow across Northern California this winter. All of that moisture has supported a lot of lush vegetation growth this spring,” AccuWeather’s lead long-range expert, Paul Pastelok, said. “That grass and brush will dry out and become potential fuel for wildfires this fall,” when any “trigger mechanism … could cause big wildfire problems.”

Slate Auto, a three-year-old Jeff Bezos-backed startup, has announced an EV truck that will cost less than $20,000 after the federal tax credit and before customization. “It’s the Burger King of trucks,” writes Car and Driver, because “it’s affordable” and “lets customers ‘have it their way’ with a lengthy accessory list, including one that turns this pickup into an SUV.”
Three weeks after “Liberation Day,” Matador Resources says it’s adjusting its ambitions for the year.
America’s oil and gas industry is beginning to pull back on investments in the face of tariffs and immense oil price instability — or at least one oil and gas company is.
While oil and gas executives have been grousing about low prices and inconsistent policy to any reporter (or Federal Reserve Bank) who will listen, there’s been little actual data about how the industry is thinking about what investments to make or not make. That changed on Wednesday when the shale driller Matador Resources reported its first quarter earnings. The company said that it would drop one rig from its fleet of nine, cutting $100 million of capital costs.
“In response to recent commodity price volatility, Matador has decided to adjust its drilling and completion activity for 2025 to provide for more optionality,” the company said in its earnings release.
In February, Matador was projecting that its capital expenditures in 2025 would be between $1.4 and $1.65 billion.This week, it lowered that outlook to $1.3 to $1.55 billion. “We’re very open to and want to have reason to grow again,” Matador’s chief executive Joseph Foran said on the company’s earnings call Thursday. “This is primarily a timing matter. Is this a temporary thing on oil prices? Or is this a new world we live in?”
Mizuho Securities analyst William Janela wrote in a note to clients Thursday morning that, as the first oil exploration and production company to report its earnings this go-round, Matador would be “somewhat of a litmus test for the sector: we don't believe the market was expecting E&Ps to announce activity reductions this soon, but MTDR's update could signal more cuts to come from peers over the next few weeks.”
West Texas Intermediate crude oil prices are currently sitting at just below $63, up from around $60 in the wake of President Donald Trump’s “Liberation Day” tariff announcements. While the current price is off its lows, it’s still well short of the almost $84 a barrel crude prices were at around this time last year.
The price decline could be attributable to any number of factors — macroeconomic uncertainty due to the trade war, production hikes by foreign producers — but whatever the cause, it has made an awkward situation for the Trump administration’s energy strategy.
The iShares U.S. Oil & Gas Exploration & Production ETF, which tracks the American oil and gas exploration industry, is down 9% for the year and more than 13% since “Liberation Day,” while the rest of the market has almost recovered as the Trump administration has indicated it may ease up on some of his more drastic tariff policies.
If other drillers follow Matador’s investment slowdown, it could imperil Trump’s broader energy policy goals.
Trump has both encouraged other countries to produce more oil (and bragged about lower oil prices) while also exhorting American drillers to “drill, baby, drill,”with enticements ranging from kneecapping emissions standards to a reduced regulatory burden.
As Heatmap has written, these goals sit in conflict with each other. Energy executives told the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas that they need oil prices ranging from $61 to $70 a barrelin order to profitably drill new wells. If prices fall further, “what would happen is ‘Delay, baby, delay,’”Wood Mackenzie analyst Fraser McKay wrote Wednesday. “We now expect global upstream development spend to fall year-on-year for the first time since 2020.”
A $65 per barrel price “dents” margins for drillers, meaning “growth capex and discretionary spend will be delayed,” McKay wrote.
Matador also announced that it had authorized $400 million worth of buybacks, and itsstock price rose some 4% on the earnings announcement, indicating that Wall Street will reward drillers who pull back on drilling and ramp up shareholder payouts.
“We’ve got the tools in the toolbox, including the share repurchase, to make Matador more value quarter by quarter,” Foran said. Rather than “blindly” pouring capital into growth, Matador would aim for a “measured pace,” he explained. “And if you mean what you say about a measured pace, that means when prices get a little lower, you take a few more moments to think about what you’re doing and don’t rush into things.”
At San Francisco Climate Week, everything is normal — until it very much isn’t.
San Francisco Climate Week started off on Monday with an existential bang. Addressing an invite-only crowd at the Exploratorium, a science museum on the city’s waterfront, former vice president and long-time climate advocate Al Gore put the significance and threat of this political moment — and what it means for the climate — in the most extreme terms possible. That is to say, he compared the current administration under President Trump to Nazi Germany.
“I understand very well why it is wrong to compare Adolf Hitler’s Third Reich to any other movement. It was uniquely evil,” Gore conceded before going on: “But there are important lessons from the history of that emergent evil.” Just as German philosophers in the aftermath of World War II found that the Nazis “attacked the very heart of the distinction between true and false,” Gore said, so too is Trump’s administration “trying to create their own preferred version of reality,” in which we can keep burning fossil fuels forever. With his voice rising and gestures increasing in vigor, Gore ended his speech on a crescendo. “We have to protect our future. And if you doubt for one moment, ever, that we as human beings have that capacity to muster sufficient political will to solve this crisis, just remember that political will is itself a renewable resource.”
The crowd went wild. Former House Speaker Nancy Pelosi took the stage and reminded the crowd that Gore has been telling us this for decades — maybe it’s time we listen. But I missed all that. Because just a few miles away, things were getting a little more in the weeds at the somewhat less exclusive venture capital-led panel entitled “The Economics of Climate Tech: Building Resilient, Scalable, and Sustainable Startups.” Here, I learned about a new iron-sodium battery chemistry and innovations in transformers for data centers, microgrids, and EV charging infrastructure.
I heard Tom Chi, founding partner of At One Ventures, utter sentences such as “parity dies because of capex inertia,” referring to the need to make clean tech not only equivalent to but cheaper than fossil-fuels on a unit economics basis. Such is the duality of climate week during the Trump administration — occasionally lofty in both its alarm and its excitement, but more often than not simply business-as-usual, interrupted by bouts of heady doom or motivational proclamations.
Some panels, like the one I moderated on the future of weather forecasting using artificial intelligence, made it a full hour without discussing Trump, tariffs, or tax credits at all. So far, that’s held true for a number of talks on how AI can be a boon to climate tech. It makes sense — the administration is excited about AI, and there’s really no indication that Trump has given any thought to either the positive or negative climate externalities of it.
But rapid data center buildout and the attendant renewables boom that it may (or may not) bring will certainly be influenced by the administration’s fluctuating policies, an issue that was briefly discussed during another panel: “AI x Energy: Gridlocked or Grid Unlocked?” Here, representatives from Softbank, Pacific Gas & Electric, and the data center builder and operator Switch touched on how market uncertainty is making it difficult to procure energy for data centers — and to figure out the cost of building a data center, period.
“There is a lot of refiguring and rereading contracts and looking at the potential exposure to things like the escalation in the cost of steel for construction projects,” Skyler Holloway of Switch said. Pinning down a price on the energy required to power data centers is also a bottleneck, Gillian Clegg, vice president of energy policy and procurement at PG&E explained. “For projects that want to connect between now and 2030, any kind of uncertainty or delay means that the generation doesn't get to the market,” Clegg said. “Maybe the load gets there first, and you have an out of balance situation.”
Everyone acknowledges that uncertainty is bad for business, and that delays related to funding, contracts, and construction can kill otherwise viable companies. But unsurprisingly, nobody here has admitted that said uncertainty might put them out of business, or even deeply in the red.Every panel I attend, I find myself wondering whether a founder or investor is finally going to raise their voice, à la Al Gore, and tell the audience that while their company’s business model is well and good, the Trump administration’s illogical antipathy towards green-coded tech and ill-conceived trade war is throwing the underlying logic — sound as it may have been just a year ago — into disarray.
None of the seven energy, food, and agricultural startups that presented at the nonprofit climate investor Elemental Impact’s main show, for instance, discussed the impacts of the administration’s policies on their businesses. Rather, they maintained a consistently upbeat tone as they described the promise of their concepts — which ranged from harnessing ocean energy to developing plant-based fertilizers to using robotics for electronics recycling — and the momentum building behind them. Nuclear and geothermal companies, seemingly poised to be the clean tech winners of Chris Wright’s Department of Energy, have been especially optimistic this week.
But really, what else can climate tech companies and investors be expected to do right now besides, well, rise and grind? It’s not like anybody has answers as to what’s coming down the policy pike. In a number of more casual conversations this week, a common sentiment I heard was that it’s not necessarily a bad time to be an early-stage startup — keep your head down, focus on research and prototyping, and reassess the political environment when you’re ready to build a pilot or demonstration plant. As for later-stage companies and venture capital firms, they’re likely working to ensure that their business models and portfolios really aren’t dependent on government subsidies, grants, or policies — as they keep assuring me is the case.
Even that might not be enough these days though. Chi said he’s always tailored his investments with At One Ventures towards companies that are viable based on unit economics alone, no subsidies and no green premium. So he wasn’t initially worried about his portfolio when Trump was elected. “None of our business models were invalidated by the election,” he said. “The only way that we could be in trouble is if they mess it up so bad that it ruins all of business, not just climate …”
Oops.
If there’s one dictum that I would expect to hold, though, it’s that the startups that make it through this period will likely be around for the long haul. I’ve been hearing that sentiment since the election, and Mona ElNagger, a partner at Valo Ventures, echoed it once again this week. “Microsoft and Apple were founded in the mid 1970s, which was a time of severe recession and stagflation. Amazon started at the tail end of a big recession in the early 1990s,” ElNagger reminded the audience at the Economics of Climate Tech panel, which she moderated. “Companies that survive and actually thrive in such periods share a common thread of resilience.”
As that panel wrapped up, things got existential once more as Chi’s talk moved from describing his investment thesis to the moment at large. “This time period in history is going to bring us tragedy after tragedy, and it’s really that moment that we’re going to understand the deep underlying structure of half of the world that we’ve built, and also the character of who we are,” Chi told the audience. It was unclear whether we were even talking about climate tech anymore. Chi continued, “It’s in that time period that we are going to step up and become whatever we are meant to be or not at all.”
The crowd sat there, a little stunned. Were we, in this very moment, becoming who we were meant to be? I took a bite of my free sushi as the networking and hobnobbing began.