You’re out of free articles.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Sign In or Create an Account.
By continuing, you agree to the Terms of Service and acknowledge our Privacy Policy
Welcome to Heatmap
Thank you for registering with Heatmap. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our lives, a force reshaping our economy, our politics, and our culture. We hope to be your trusted, friendly, and insightful guide to that transformation. Please enjoy your free articles. You can check your profile here .
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Subscribe to get unlimited Access
Hey, you are out of free articles but you are only a few clicks away from full access. Subscribe below and take advantage of our introductory offer.
subscribe to get Unlimited access
Offer for a Heatmap News Unlimited Access subscription; please note that your subscription will renew automatically unless you cancel prior to renewal. Cancellation takes effect at the end of your current billing period. We will let you know in advance of any price changes. Taxes may apply. Offer terms are subject to change.
Create Your Account
Please Enter Your Password
Forgot your password?
Please enter the email address you use for your account so we can send you a link to reset your password:
The all-American EV startup is cutting costs to survive.

America’s most interesting electric-vehicle company is about to have the defining year of its life.
On Wednesday, the company reported that it lost $1.58 billion in the fourth quarter of last year, bringing its net annual losses to $5.4 billion. It announced that it is laying off about 10% of its salaried employees, but — at the same time — promised that it has a plan to achieve a small profit by the end of this year.
Rivian does not seem to be in trouble — not quite yet, at least. But the earnings made clear what electric-vehicle observers have known for a long time: Either the company will emerge from this year poised to be a winner in the EV transition, or it will find itself up against the wall.
That’s partially because Rivian has a stomach-turning number of corporate milestones coming up. Over the next 11 months, it plans to unveil an entirely new line of vehicles, shut down its factory for several weeks for cost-saving upgrades, break ground on a new $5 billion facility in Georgia, and — most importantly — turn a profit for the first time. It also expects to manufacture and deliver roughly another 60,000 vehicles to customers.
Any one of these goals would be difficult to achieve in any environment. But Rivian is going to have to execute all of them during a time defined by “economic and geopolitical uncertainties” and especially high interest rates, its CEO R.J. Scaringe told investors on Wednesday. Since 2021, Rivian’s once robust stockpile of cash has been cut in half to about $7 billion; at its current burn rate, the company will run out of money in a little more than two years.
Although Rivian’s situation is dire, it’s not experiencing anything out of the ordinary. As I’ve written before, the electric truck maker is crossing what commentators sometimes call “the EV valley of death.” This is the challenging point in a company’s life cycle where it has developed a product and scaled it up to production — thereby raising its operating expenses to eye-watering levels — but where its revenue has not yet increased too.
During this vulnerable period, a company essentially burns through its cash on hand in the hope that more customers and serious revenue will soon show up. If those customers don’t arrive, then it either needs to raise more cash … or it runs out of money and goes bankrupt.
It’s a frightening time, but once a company crosses the valley of death, it can reach an idyll. Not so long ago, Tesla found itself in something like Rivian’s position as it prepared to launch the Model 3. Seven years later, it is the most valuable automaker in the world.
Once Rivian’s revenue exceeds its costs, its problems will get easier, or at least more straightforward: Instead of fighting for its survival and watching its cash reserves dwindle, Scaringe will be able to make more strategic trade-offs. Should the company cut costs to expand its profit margin and reward investors, or should it pass the savings along to customers in the form of lower prices, thus growing its market share? Scaringe can’t make these types of decisions until his firm is safely out of the valley.
Claire McDonough, Rivian’s chief financial officer and a former J.P. Morgan director, has a plan for crossing that canyon — an aptly if strangely named “bridge to profitability” that it will attempt to build this year. Rivian’s survival, she said, will depend above all on cutting the unit costs of producing its vehicles, including by using fewer materials to make every car. Other savings will come from making more vehicles faster. That’s what makes the shutdown plan, though it might seem extreme, worth it; McDonough said those improvements alone will get the company about 80% of the way to profitability.
Another 15% will come from marketing more “software-enabled products” to Rivian drivers and by selling air-pollution credits to other carmakers, whose vehicles are not as climate-friendly. This is a tried-and-true technique; Tesla first turned a profit in 2021 by selling regulatory credits needed to comply with federal and California state-level rules to other, dirtier automakers. But that same year, Tesla also debuted an entirely new vehicle: the Model Y crossover, which quickly became its top seller in the United States. Tesla, in other words, finally started to make money by cutting costs, finding new revenue sources, and releasing new products.
New products, however, are becoming a weak point for Rivian. The company says that high interest rates will keep demand for its vehicles flat this year. It expects to make about 60,000 of them, about 20,000 fewer than what it had once anticipated. The Rivian R1S, a three-row S.U.V., has become the company’s flagship; it is selling better and is cheaper to manufacture than Rivian’s pickup, the R1T. It also costs at least $75,000, or nearly $600 a month to lease. The highest-tier models can cost $99,000. Turns out, it’s difficult to sell a lot of $70,000 trucks when even the cheapest new-car loans hover around 6%.
Rivian once had a first-to-market advantage in the electric three-row SUV market, but that may be fizzling out, too. Kia is now selling its own all-electric three-row SUV, the EV9, for $18,000 less than the R1S; in fact, the Kia EV9’s most expensive trim costs $76,000, which is only slightly more than the cheapest R1S. The Kia SUV can also charge faster than the Rivian under ideal conditions. It remains an open question how many rich suburbanites are still interested in buying Rivians, especially now that the Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning are competing directly with Rivian’s pickup truck.
The company’s hopes, in other words, rest on its next product line: the R2, which it will launch on March 7. We know almost nothing about the R2 line, except that it will probably include an SUV, that it will go on sale in 2026, and that it will fall somewhere in the $45,000 to $55,000 price range. (The median new car transaction in the United States now costs $48,200.) Last year, Scaringe told me that the R2’s timing was perfect because it would fit “beautifully with what we see as this big shift” in the American EV market. In today’s market, he said, “a lot of people ask themselves, Am I gonna get an electric car? Well maybe the next one.” He better hope they’ll start buying that next one in 2026.
Even if they do, Rivian may still have to confront the problem that Tesla has changed the EV market before Rivian could get there. When the first Tesla Model 3s were delivered in 2017, the sedan was instantly one of the best EVs on the market — because it was one of the only EVs on the market. Now every automaker in the world has plans to compete at the Model 3’s price point.
Rivian’s fortunes don’t rest entirely on American consumers; it also sells vans to commercial fleet operators, as well as delivery trucks to Amazon. (Amazon owns about 17% of Rivian.) But that business can be lumpy. Rivian’s vehicle growth slowed down last quarter, for instance, almost entirely because of a near pause in sales to Amazon, which sets up fewer new vehicles in the fourth quarter. If Amazon is willing to bail out Rivian, in other words, it’s not yet clear in the data.
None of this is to say that the company’s outlook is dire. Rivian was always going to find itself at a moment like this, when its expenses exceeded its revenue by such a large amount. The automaker already has devoted fans, and many people — myself included — are interested in the R2 as a potential first EV purchase.
And the company has shown that it can make strides in a single year. Twelve months ago, I had never seen a Rivian on the road before; today, one is regularly parked on my block. The company rocketed from a standing start to become the No. 5 best-selling electric car brand in America last year. What the company has done so far is impressive. But now it must prove that it can be great.
Editor's note: This story has been updated to correctly reflect Rivian's cash burn rate.
Log in
To continue reading, log in to your account.
Create a Free Account
To unlock more free articles, please create a free account.
Did a battery plant disaster in California spark a PR crisis on the East Coast?
Battery fire fears are fomenting a storage backlash in New York City – and it risks turning into fresh PR hell for the industry.
Aggrieved neighbors, anti-BESS activists, and Republican politicians are galvanizing more opposition to battery storage in pockets of the five boroughs where development is actually happening, capturing rapt attention from other residents as well as members of the media. In Staten Island, a petition against a NineDot Energy battery project has received more than 1,300 signatures in a little over two months. Two weeks ago, advocates – backed by representatives of local politicians including Rep. Nicole Mallitokis – swarmed a public meeting on the project, getting a local community board to vote unanimously against the project.
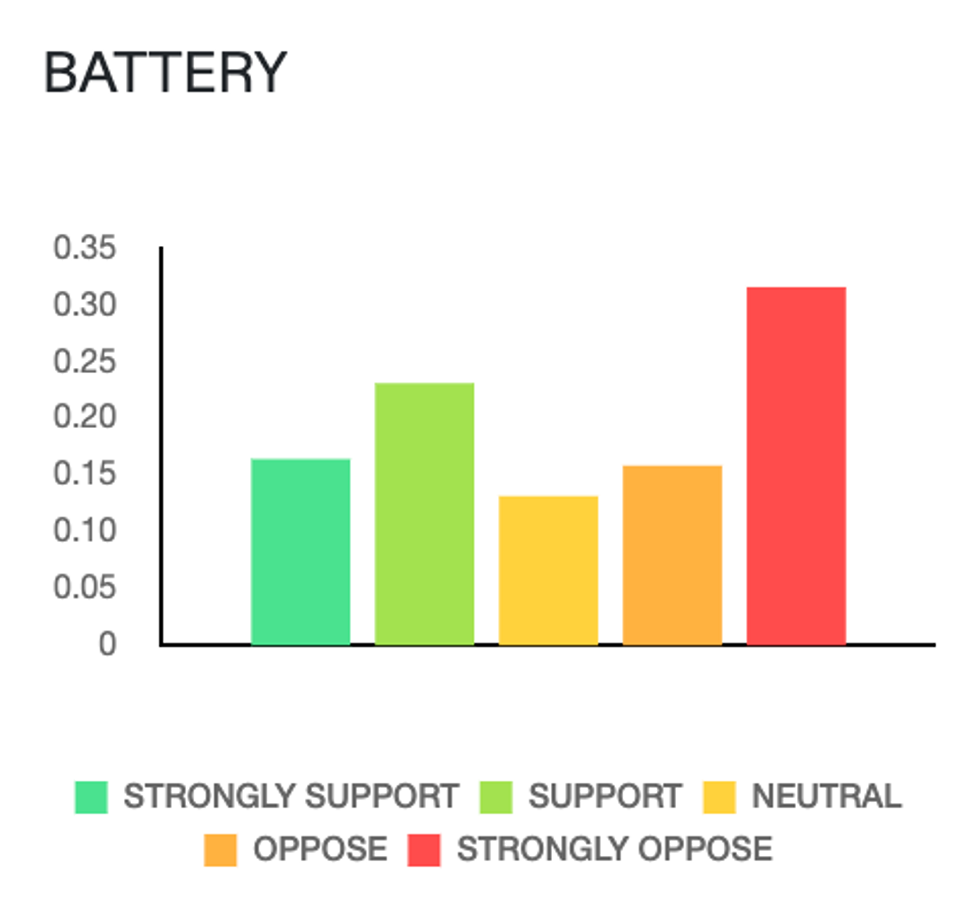
According to Heatmap Pro’s proprietary modeling of local opinion around battery storage, there are likely twice as many strong opponents than strong supporters in the area:
Yesterday, leaders in the Queens community of Hempstead enacted a year-long ban on BESS for at least a year after GOP Rep. Anthony D’Esposito, other local politicians, and a slew of aggrieved residents testified in favor of a moratorium. The day before, officials in the Long Island town of Southampton said at a public meeting they were ready to extend their battery storage ban until they enshrined a more restrictive development code – even as many energy companies testified against doing so, including NineDot and solar plus storage developer Key Capture Energy. Yonkers also recently extended its own battery moratorium.
This flurry of activity follows the Moss Landing battery plant fire in California, a rather exceptional event caused by tech that was extremely old and a battery chemistry that is no longer popular in the sector. But opponents of battery storage don’t care – they’re telling their friends to stop the community from becoming the next Moss Landing. The longer this goes on without a fulsome, strident response from the industry, the more communities may rally against them. Making matters even worse, as I explained in The Fight earlier this year, we’re seeing battery fire concerns impact solar projects too.
“This is a huge problem for solar. If [fires] start regularly happening, communities are going to say hey, you can’t put that there,” Derek Chase, CEO of battery fire smoke detection tech company OnSight Technologies, told me at Intersolar this week. “It’s going to be really detrimental.”
I’ve long worried New York City in particular may be a powder keg for the battery storage sector given its omnipresence as a popular media environment. If it happens in New York, the rest of the world learns about it.
I feel like the power of the New York media environment is not lost on Staten Island borough president Vito Fossella, a de facto leader of the anti-BESS movement in the boroughs. Last fall I interviewed Fossella, whose rhetorical strategy often leans on painting Staten Island as an overburdened community. (At least 13 battery storage projects have been in the works in Staten Island according to recent reporting. Fossella claims that is far more than any amount proposed elsewhere in the city.) He often points to battery blazes that happen elsewhere in the country, as well as fears about lithium-ion scooters that have caught fire. His goal is to enact very large setback distance requirements for battery storage, at a minimum.
“You can still put them throughout the city but you can’t put them next to people’s homes – what happens if one of these goes on fire next to a gas station,” he told me at the time, chalking the wider city government’s reluctance to capitulate on batteries to a “political problem.”
Well, I’m going to hold my breath for the real political problem in waiting – the inevitable backlash that happens when Mallitokis, D’Esposito, and others take this fight to Congress and the national stage. I bet that’s probably why American Clean Power just sent me a notice for a press briefing on battery safety next week …
And more of the week’s top conflicts around renewable energy.
1. Queen Anne’s County, Maryland – They really don’t want you to sign a solar lease out in the rural parts of this otherwise very pro-renewables state.
2. Logan County, Ohio – Staff for the Ohio Power Siting Board have recommended it reject Open Road Renewables’ Grange Solar agrivoltaics project.
3. Bandera County, Texas – On a slightly brighter note for solar, it appears that Pine Gate Renewables’ Rio Lago solar project might just be safe from county restrictions.
Here’s what else we’re watching…
In Illinois, Armoracia Solar is struggling to get necessary permits from Madison County.
In Kentucky, the mayor of Lexington is getting into a public spat with East Kentucky Power Cooperative over solar.
In Michigan, Livingston County is now backing the legal challenge to Michigan’s state permitting primacy law.
On the week’s top news around renewable energy policy.
1. IRA funding freeze update – Money is starting to get out the door, finally: the EPA unfroze most of its climate grant funding it had paused after Trump entered office.
2. Scalpel vs. sledgehammer – House Speaker Mike Johnson signaled Republicans in Congress may take a broader approach to repealing the Inflation Reduction Act than previously expected in tax talks.
3. Endangerment in danger – The EPA is reportedly urging the White House to back reversing its 2009 “endangerment” finding on air pollutants and climate change, a linchpin in the agency’s overall CO2 and climate regulatory scheme.